What is ISO 13485:2016?
ISO 13485:2016 is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for the Quality Management System (QMS) of organizations involved in the manufacturing, distribution, servicing, and disposal of medical devices. Organizations with ISO 13485:2016 certification are recognized to produce medical devices that are at par with industry standards.
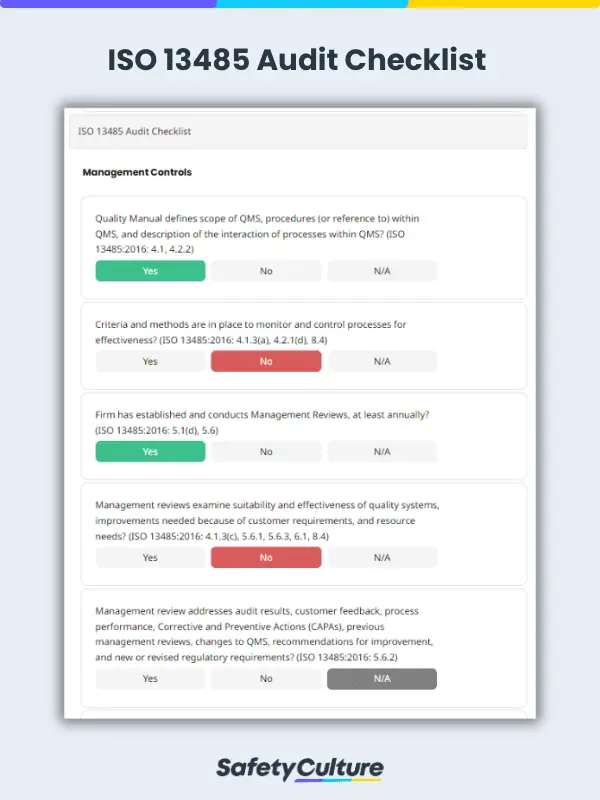
What is an ISO 13485:2016 Audit Checklist?
An ISO 13485:2016 audit checklist is a tool used by quality managers to determine if the organizations’ QMS for medical devices aligns with the requirements of the ISO 13485:2016 standard. The checklist includes a comprehensive list of questions, criteria, or statements that are useful in evaluating readiness for a third-party ISO 13485:2016 certification audit.
Benefits of Using a Checklist During ISO 13485 Audits in Your Organization
ISO 13485 audit checklists play a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness and compliance of an organization’s QMS for medical devices, as well as its process of auditing. Apart from that, here are more key reasons why using these checklists is important:
- Helps auditors conduct a thorough evaluation of the QMS
- Verifies compliance with the standard’s requirements
- Promotes standardization and consistency across audits
- Assists auditors to identify areas of non-compliance, gaps, and areas for continuous improvement within the organization’s current practices
- Ensures proper documentation and evidence collection during audits
- Prepares organizations for external audits and certification assessments
What Should be Included in an ISO 13485 Audit Checklist?
An ISO 13485 audit checklist should cover various aspects of a quality management system (QMS) for medical devices to ensure compliance with the ISO 13485 standard. While the specific items on the checklist may vary based on the organization’s unique processes and activities, here are key areas that should typically be included:
- Title Page
- Management Responsibility
- Design and Development/Design Controls
- Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
- Control of Non-Conforming Products
- Medical Device Reporting (MDR)
- Production and Process Controls (P&PC)
- Monitoring and Measurement
- Sterilization Process Controls
- Purchasing Controls
- Documentation and Records
- Customer Requirements
- Technical Files
- Risk Management
- Completion Page
5 Steps to Prepare for ISO 13485:2016 Certification
Now, what must organizations keep in mind and consider when getting ready to obtain a certification in ISO 13485? Here are some steps they can take:
- Obtain a copy and gain an understanding of the ISO 13485:2016 standard.
- Identify areas for improvement in the current QMS by conducting a gap analysis or a readiness audit to ensure compliance with the ISO 13485:2016 regulatory requirements.
- Perform quality monitoring audits and maintain a record of the results.
- Define your organization’s competencies and determine training requirements for ISO 13485:2016 certification based on the internal audit results.
- Ensure competence needs are met and that all parties involved are kept in the loop.
It’s also crucial to note that these steps aim to guide your organization on what to prioritize doing toward an ISO 13485 certification. However, you may add more processes or necessary audits to complement your efforts in maintaining a working and safe QMS.
How to Use a Checklist for ISO 13485 Compliance
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use an ISO 13485 audit checklist:
- Familiarize yourself with the checklist to understand the questions or criteria it includes. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of the requirements of ISO 13485 to effectively use it, too.
- Assess your current processes and activities against the checklist. Compare your practices with the requirements outlined in the checklist and identify areas where your organization may have gaps or areas for improvement.
- Document evidence to demonstrate compliance with each checklist item. This may include records, procedures, work instructions, training records, or other relevant evidence.
- Conduct a self-assessment of your organization’s QMS and determine whether your organization meets the requirements or if there are areas that need improvement.
- Identify specific corrective actions to address issues such as non-compliance or areas requiring improvement and develop an action plan for implementing the necessary changes and improvements.
- Execute the corrective actions according to the action plan to ensure that the identified improvements are implemented effectively and within the designated timelines.
- Validate the effectiveness of the changes by conducting internal audits or reviews to ensure that the improvements have addressed the non-compliances and have resulted in a more compliant QMS.
- Continuously monitor and review your QMS to ensure ongoing compliance with ISO 13485.
- Regularly review and update the checklist to align with any revisions in the ISO 13485 standard or changes in your organization’s processes.
FAQs About ISO 13485 Audit
While using checklists for conducting ISO 13485 audits isn’t required, they are highly recommended as useful tools to help ensure compliance with the standard. The audit checklist provides a straightforward and detailed list of elements and aspects to check in an organization’s QMS, making it easier for auditors to ensure everything is accounted for.
The frequency of using ISO 13485 checklists depends on the organization’s needs and internal requirements. Some may choose to conduct self-assessments using an ISO 13485 internal audit checklist periodically, such as annually, while others may incorporate it into their ongoing monitoring and improvement processes.
An ISO 13485 audit is an in-depth assessment process that allows organizations to ensure compliance with the current QMS standard for medical device manufacturing. This process is performed to help businesses prepare for and obtain ISO 13485 certification.
After obtaining the initial ISO 13485 certification, regular surveillance audits are conducted at least once a year to ensure the organization’s continued compliance with the standard. Recertification audits, on the other hand, are performed every three years.
Third-party or external auditing organizations conduct the audits for the actual ISO 13485 certification. The initial audits, however, are performed by internal auditors—mostly those in the quality assurance team—in preparation for the subsequent and more formal assessments.