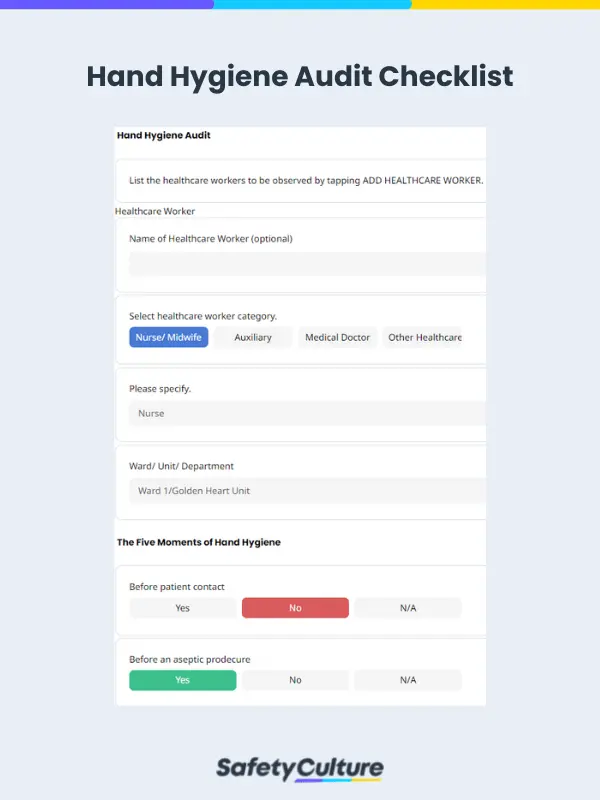
What is Hand Hygiene Audit?
A hand hygiene audit ensures that healthcare professionals adhere to recommended hand hygiene practices, particularly those outlined in the WHO’s 5 Moments of Hand Hygiene. Hand hygiene audit aims to prevent the spread of infection between healthcare workers and patients through observational inspections of handwashing techniques.
What is Hand Hygiene Compliance?
Hand hygiene compliance is a health and safety policy that is required of health care providers. This policy helps in reducing incidences of health-related infections, therefore protecting both patient and healthcare workers. It may seem like a simple policy, however, negligence to it will negatively impact a healthcare institution’s morbidity rate, duration of hospital stays, and treatment prices.
In a study about Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control, it was concluded that a good hand hygiene compliance is achieved when health care providers are well trained and have better knowledge and understanding of the hand hygiene guidelines and techniques. Other factors that affect compliance are the attitude of healthcare providers towards hand hygiene, and the presence of soap and water, and alcohol or sanitizers in the working area.
Why Perform the Audits?
While easily avoidable, acquiring infection during the ordinary course of patient care remains a leading cause of death and disability worldwide – with over 1.4 million cases occurring at any given time. The simplest and most effective solution to prevent the spread of infection in healthcare is for healthcare workers to practice proper hand hygiene techniques during the five moments of patient care.
Healthcare facilities should perform regular hand hygiene audits to identify training gaps and remind staff of the importance of basic infection control.
How to Perform a Hand Hygiene Audit
Based on the World Health Organization (WHO) hand hygiene guidelines for 2019, the WHO recommends these key steps to follow when performing a hand hygiene audit of healthcare workers:
1. Communicate with the facility
Contact the hospital administration before commencing the audit. Announce the period of observation and the purpose of performing the hand hygiene audit. Inform healthcare workers about the data documentation method (e.g. photo evidence).
2. Identify specific areas to audit
Audit all areas where patient care is regularly undertaken. Introduce yourself to the head nurse, the chief doctor of the unit or the department manager and provide a general explanation of the role of the observer. Aim to perform a sufficient number of observations across various wards and departments.
3. Maintain patient privacy
Patient privacy must not be compromised during auditing. Written permission from patients may be required. Do not audit during extreme situations (e.g. emergency medical treatment, signs of uncontrolled stress in a healthcare worker).
4. Observe an individual healthcare worker
Conduct the audit according to the WHO’s Five Moments of Hand Hygiene:
- Before touching a patient
- Before clean/aseptic procedures
- After body fluid exposure/risk
- After touching a patient
- After touching patient surroundings
Indicate whether or not the healthcare worker used the following techniques:
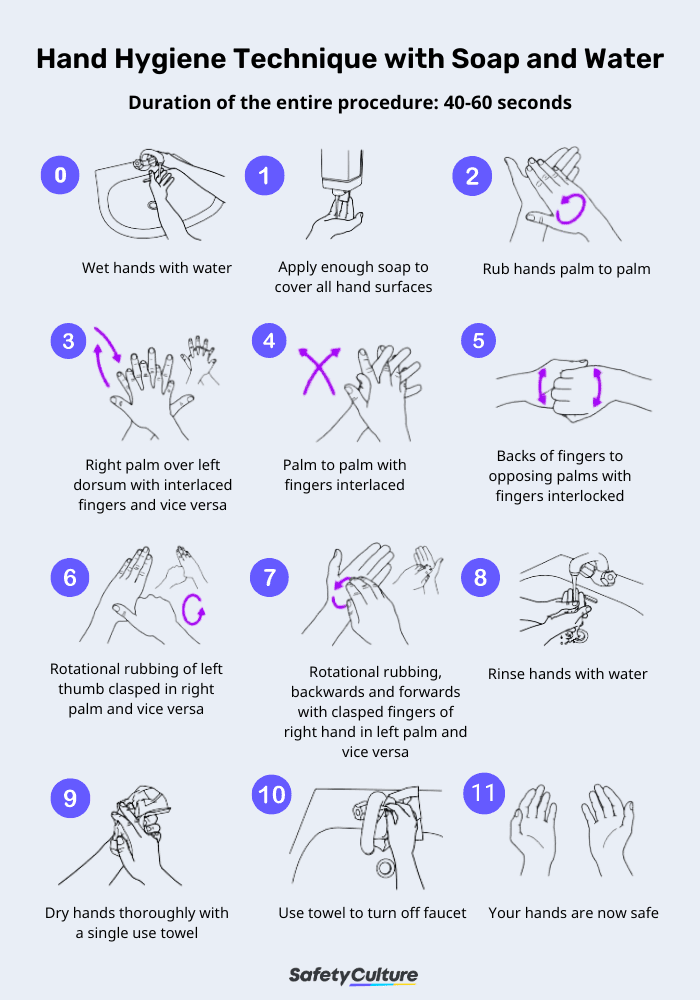
Hand Hygiene Technique | WHO
5. Document and share key findings
Provide feedback to the healthcare worker if hand hygiene was not performed. Compliance scores can be determined by the ratio of the number of performed actions (hand hygiene) to the number of opportunities (moments). Results should be shared with management, department heads, boards as well as front-line healthcare workers.