What is a BRC Audit?
A BRC Audit, or BRC Food Safety Audit, is BRC’s official assessment of a food manufacturer’s adherence to its Global Standard for Food Safety. Conducted by an accredited certification body, this practice thoroughly examines all processes and documents involved in the nine core areas of food manufacturing operations.
What is a BRC Audit Checklist?
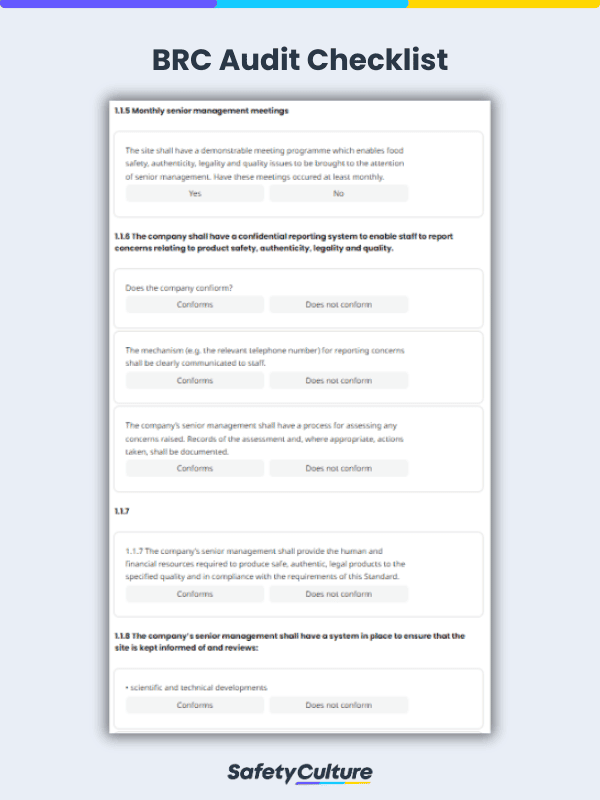
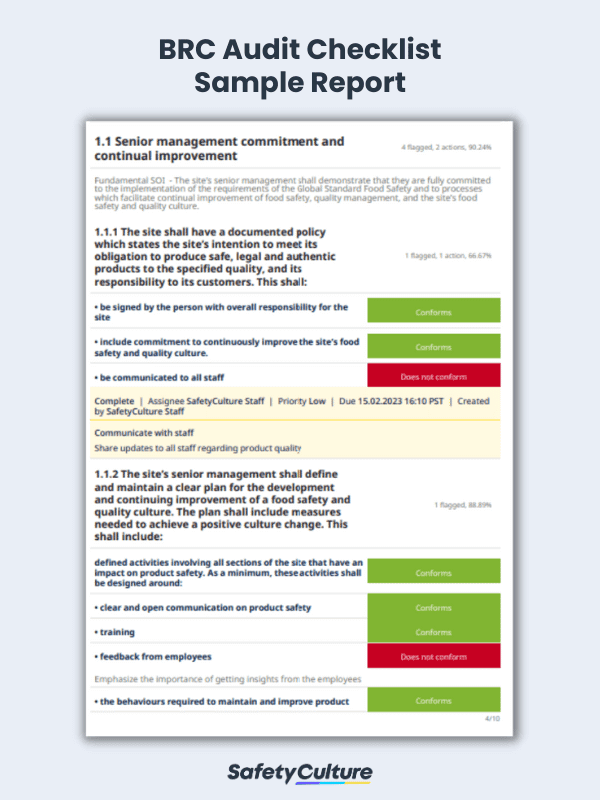
A BRC audit checklist is a tool that food manufacturing businesses can use to perform regular inspections in preparation for a certification audit. With a comprehensive audit checklist, food manufacturers can proactively spot non-conformance, determine unsafe food production methods, or identify areas for improvement and immediately correct them to comply with the current BRC standards.
What Does a BRC Audit Checklist Include?
The latest version of BRC, issue 9, emphasizes the importance of creating a culture of safety and striving for continuous improvement. Since each BRC clause has a specific set of requirements, they should be reflected in a BRC audit checklist. In detail, issue 9 highlights the following requirements:
- Clause 1: Management Commitment – leaders of companies should help ensure the implementation and continuous improvement of food safety processes.
- Clause 2: The Food Safety Plan: HACCP – implementing HACCP can help identify and manage risks in food production.
- Clause 3: Food Safety and Quality Management System – proper documentation of processes in place helps manage the safety of food production and keep staff properly informed.
- Clause 4: Site Standards – setting and maintaining the ideal site for food production
- Clause 5: Product Control – setting controls in place, such as allergen management and product testing.
- Clause 6: Process Control – this is ensuring that the documented HACCP plan is consistently followed to maintain product quality.
- Clause 7: Personnel – ensure that employees are trained, wearing PPE, and following proper hygiene.
- Clause 8: Production Risk Zones – ensure that products susceptible to pathogen contamination have control measures to improve safety.
- Clause 9: Traded Products – ensure sites that purchase and sell food products properly process and pack them to avoid contamination.
How to Prepare for a BRC Audit
Since there is a lot of information and details to take into consideration to ensure an effective BRC audit, take note of the following tips:
- Prepare proper documentation and records that prove the consistent implementation of food safety management.
- Review and be familiar with the latest BRC version.
- Conduct internal audits in order to identify gaps and improve on them.
- Get in touch with a third-party auditor who will conduct the BRC audit for certification.
- Leverage new technology, such as software and digital checklists, to perform audits.
FAQs About BRC Food Safety
BRC stands for the British Retail Consortium, a company formed by retailers that created a standard for food safety intended for businesses involved in food production.
BRC certification is a recognition given to businesses that have been audited and found to have met the BRC global standard for food safety.
Both schemes require a regularly evaluated and continuously improved upon: 1) food safety management system; 2) good manufacturing, distribution, and agricultural practices; and 3) HACCP system.
BRC is more prescriptive on procedures and guidelines to follow for food safety while FSSC 22000 emphasizes a framework approach—helping a business implement its own system.