What is an Office Risk Assessment?
An office risk assessment is a systematic process performed by office managers and administrators to ensure that the work environment is free from health and safety threats. This process entails regular checks of the site facilities and equipment, employee awareness to safety rules, and adherence to security measures. Office risk assessments can help businesses create a safer, comfortable, and more cost-efficient office-based environment.
Using a Template
An office risk assessment template is a tool that aids office managers in ensuring the completion of tasks that involve a systematic examination of office activities to identify hazards and associated risks. It is used to record the likelihood of risks and corresponding control measures to prevent office incidents, accidents, or near misses.
What is the Purpose of It?
Office risk assessments are vital to ensure a safe and healthy work environment for office workers. It is employers’ legal duty to provide a hazard-free workplace that complies with standards, rules, and regulations issued under the OSH Act. Proper implementation of general office risk assessment can:
- help improve office safety;
- boost employee productivity and efficiency;
- provide information for office safety training; and
- help identify and evaluate hazards to implement corrective action to remove or minimize the level of risks.
What are the Risks of Working in an Office?
Workplace safety is paramount in every business. Commonly, people think, an office workplace is a hazard-free place, but on contrary, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there are tens of thousands of work-related health problems and injuries office workers are suffering from each year. Identifying the causes of these hazards can help employees prevent unexpected incidents. Below are the six main categories of workplace hazards.
- Physical – this hazard involves temperature; air quality; ventilation; noise; and slips, trips, and falls. Temperatures can change the mood of an employee if it starts to feel uncomfortable, this can result in low productivity and morale. Clutter can cause accidents including slips, trips, and falls.
- Safety – this hazard involves unsafe working conditions including fire and electrical risks.
- Biological – this hazard includes viruses or bacteria that can cause adverse health impacts. Employees can suffer from communicable diseases through overexposure to human waste, molds, or cytotoxic substances.
- Ergonomic – this hazard involves employees spending many hours a day seated at a desk which may cause musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs).
- Psychosocial – this hazard includes employee mental health and well-being such as stress, harassment, or workplace violence.
- Chemical – this hazard can result in both physical and health impacts. Exposure to hazardous chemicals such as Formaldehyde, 2-Butoxyethanol, Sodium Hydroxide, and others when performing workplace housekeeping can cause skin irritation, respiratory system irritation, and blindness.
7 Most Common Office Risks and How to Handle Them
Like other work setups, an office-based environment poses numerous hazards which are business-impacting and can potentially harm workers. Here are some of the most common risks found in an office work situation and tips on how to deal with them:
- Slipping and tripping on spillages and objects – this issue can be solved by keeping a good housekeeping practice. Ensure no trailing cables, well-lit areas, and clear paths and walkways from obstructions.
- Manual handling of heavy materials – assess yourself if you can lift the heavy material or not. Do not hesitate to call for assistance if needed.
- Poorly designed workstations – monitor the ergonomic practices of staff when sitting and using computers. Learn more about good ergonomic practices.
- Falling from heights – falls from any height can cause bruising and fractures. Check if chairs and ladders are in good working order. Ask assistance from authorized personnel if possible.
- Stress-related hazards – this includes bullying, lack of job control, etc. HR personnel must develop policies and initiate training on stress and how to cope with it.
- Electrical and fire hazards – these two hazards often go along due to faulty equipment and machine explosion causing burns, fires, and even fatalities. All employees must be trained to report all hazards that may cause danger to workers.
- Working alone – certain office jobs require some staff to work by themselves. Managers should conduct safety inspections and check the medical condition of the lone worker before commencing work. Find out more.
5 Easy Steps on How to Conduct an Office Risk Assessment
To manage the health and safety of the business, it is the employer’s responsibility to control and deal with the risks in the workplace. Think about what might cause harm to people and decide whether the controls in place help prevent harm to the workers. The Health and Safety Executive (HSE) has developed five basic steps to carry out an office risk assessment more effectively:
-
- Identify the hazards by conducting walkthroughs and site visits;
- Record who could be harmed by hazards and how;
- Document all existing controls in place and determine what else is needed;
- Prioritize what hazards need to be mitigated then take action and
- Document and review all findings. Monitor all risks actioned
- Creating a Safer Office Working Environment with SafetyCulture
Example Assessment
An office risk assessment can be conducted to analyze any risks associated with office work activity. It helps evaluate scenarios to proactively implement control measures and prevent any issues that can potentially harm workers or can negatively impact the business.
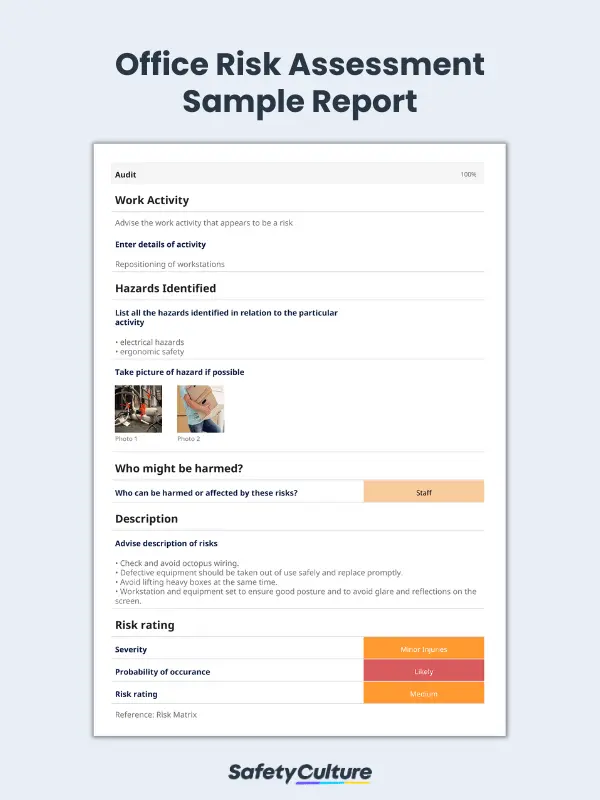
Here is a scenario in which an office manager conducts an office health and safety risk assessment following the activity of setting up a workstation for new employees. The manager uses an office risk assessment template to record the details of the inspection and perform the following:
- Document potential risks that he spots on site. (e.g. electrical and ergonomic hazards).
- Evaluate the risk by using a risk matrix to identify the severity, likelihood, and risk rating of the recorded risk.
- After the evaluation, he recommends implementing administrative controls to eliminate the risks that can potentially harm his staff such as following the 10 principles of ergonomic safety.
- Complete the assessment by asking his staff to report any musculoskeletal symptoms they may encounter over time.