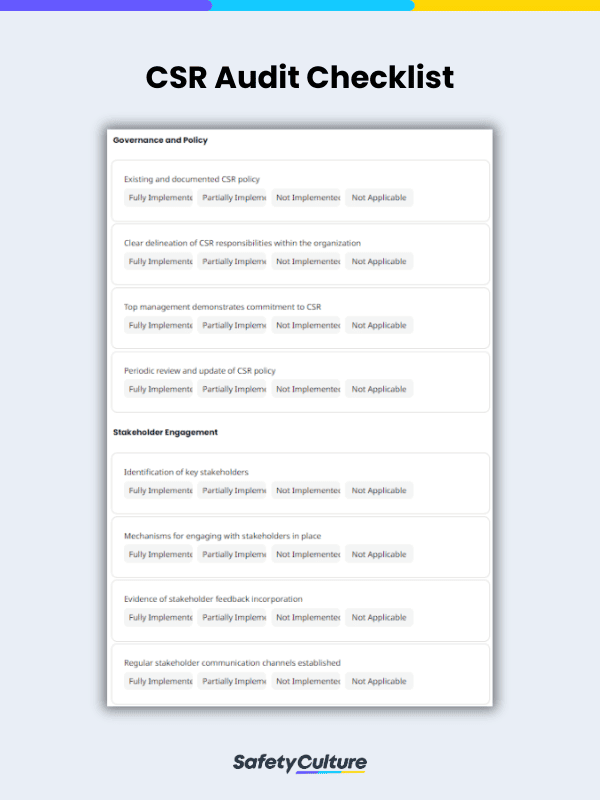
What is a CSR Audit Checklist?
A CSR audit checklist is a structured tool designed to assess and evaluate an organization’s commitment to ethical, social, and environmental responsibilities. It consists of a set of questions or items to guide the examination of various aspects of a company’s operations to ensure alignment with socially responsible practices. By using a checklist, businesses can enhance transparency, accountability, and sustainability, fostering positive relationships with stakeholders and demonstrating a commitment to responsible corporate citizenship.
Why Use a Checklist for Auditing an Organization’s CSR Practices
Regular audits using the checklist contribute to continuous improvement in CSR practices and help organizations align with global sustainability standards. Such standards include the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) which provide guidelines for CSR reporting and align with CSR audit checklists.
Organizations can also use CSR audit checklists as complementary tools when checking their conformance with ISO 26000, a set of guidelines created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that provides a framework for establishing social responsibility and sustainable development practices.
Aside from those, using a CSR checklist for auditing an organization’s CSR practices offers the following benefits:
Systematic Evaluation
A checklist guides auditors through each critical aspect, ensuring a thorough examination of governance, stakeholder engagement, ethical business practices, and environmental responsibility. This systematic process reduces the likelihood of oversight and contributes to a comprehensive assessment.
Consistency and Standardization
By providing a standardized framework, a checklist helps ensure that each audit follows the same guidelines, allowing organizations to compare results over time. This consistency enhances the reliability of the audit process and facilitates a more objective evaluation.
Efficiency and Continuous Improvement
The use of a checklist also allows auditors to focus on specific criteria without getting overwhelmed, enabling a quicker and more targeted evaluation. Moreover, the checklist’s documentation of gaps and weaknesses supports organizations in implementing corrective actions, fostering a culture of continuous improvement in CSR practices.
What to Include in a CSR Audit Checklist
In creating a CSR audit checklist, organizations must focus on specific aspects to help improve their transparency and accountability in their CSR initiatives. To ensure a thorough audit, the following sections and elements must be included in the checklist:
- Title Page
- Governance and Policy
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Ethical Business Practices
- Labor Practices
- Environmental Responsibility
- Supply Chain Responsibility
- Social Impact and Community Development
- Philanthropy and Volunteering
- Human Rights
- Reporting and Transparency
- Continuous Improvement
- Legal Compliance
- Completion Page
How to Create and Use One
Utilizing a CSR audit checklist involves a systematic process to ensure comprehensive coverage of ethical, social, and environmental practices within an organization. Here’s a step-by-step guide you can follow on how to effectively create and use a checklist for CSR audits:
- Break down CSR into key components such as governance, stakeholder engagement, ethical business practices, labor practices, environmental responsibility, and more.
- Engage with internal and external stakeholders to gather input on CSR expectations and priorities. Make sure to incorporate their feedback to ensure the checklist reflects diverse perspectives.
- Provide training to auditors on how to use the checklist effectively so that they’ll understand the importance of objectivity and consistency during the audit process.
- Conduct a pilot audit using the checklist internally to identify any ambiguities, redundancies, or gaps.
- Go through each item on the checklist systematically and use the response choices to indicate the status of each criterion.
- Develop a continuous improvement plan based on audit findings by outlining specific actions to address identified gaps and enhance CSR performance.
- Prepare a comprehensive report summarizing the audit results, including strengths, weaknesses, and improvement plans, to relevant stakeholders, both internally and externally.
- Share the results of the CSR audit, including successes and challenges, with stakeholders.
- Periodically review and update the CSR audit checklist to keep it aligned with evolving CSR standards and organizational priorities.
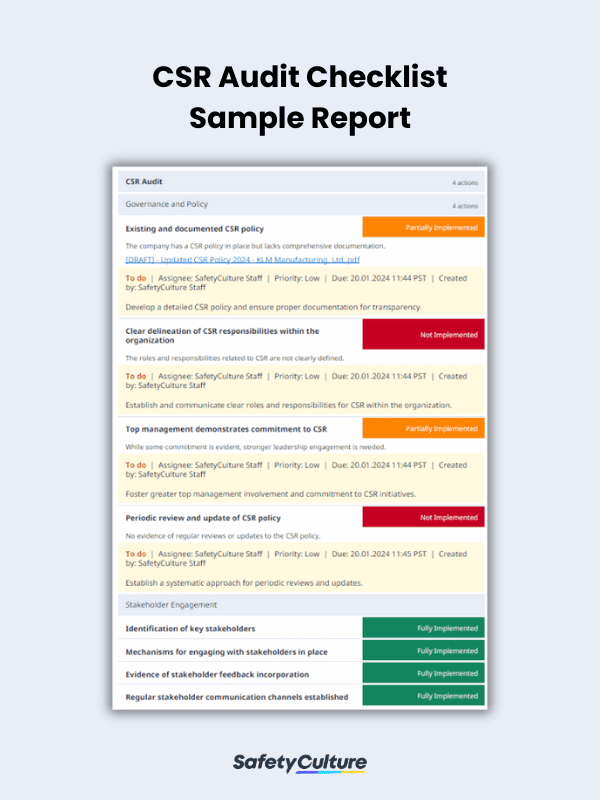
CSR Audit Checklist Template Example
If you’re wondering what a checklist for CSR audits looks like, gain insights into the key elements to consider including and utilizing in it using this sample CSR report template when filled out and completed:
FAQs About CSR Audit Checklists
The implementation of CSR audit checklists within an organization is typically handled by the CSR team or department, if one exists. However, the overall commitment and integration of CSR practices often require the support and involvement of top management. In successful organizations, there’s a collaborative effort involving various departments, with key roles played by executives, CSR professionals, and relevant stakeholders. The active engagement of leadership ensures that CSR practices are integrated into the organization’s culture and strategic decision-making processes.
Larger organizations with more extensive operations might opt for a more detailed checklist to assess their diverse activities comprehensively. In contrast, smaller organizations may choose a simpler version, focusing on fundamental CSR elements. The adaptability and customization of a CSR audit checklist for different organizational sizes are essential and allow organizations to align the checklist with their specific needs.
Yes, a CSR audit checklist can provide a structured framework for organizations to assess their CSR practices in comparison to established standards within their sector. Aligning a CSR audit checklist with industry standards ensures that the organization’s social and environmental responsibilities are in line with the expectations of stakeholders and industry peers, contributing to overall sustainability and responsible business practices.
Penalties for CSR non-compliance may include damage to the organization’s reputation, loss of stakeholder trust, negative impact on brand value, and potential consequences in terms of attracting socially conscious customers, partners, or investors. In some cases, legal actions may also be necessary if non-compliance with specific CSR-related laws or regulations is identified during the audit.
Organizations should update their CSR audit checklists at least annually to ensure that the checklist remains a dynamic and effective tool for assessing CSR practices. However, more frequent updates may be necessary if there are significant changes in the organization’s operations, industry regulations, or global sustainability standards.